What is AIoT and What Are Its Differences from Edge Gateways?
To understand the differences between AIoT and Edge Gateways, it is first essential to clarify the core definitions and technical scopes of the two. The former is a macroscopic technical system, while the latter is a specific functional component, and they occupy different layers in the Internet of Things (IoT) architecture.
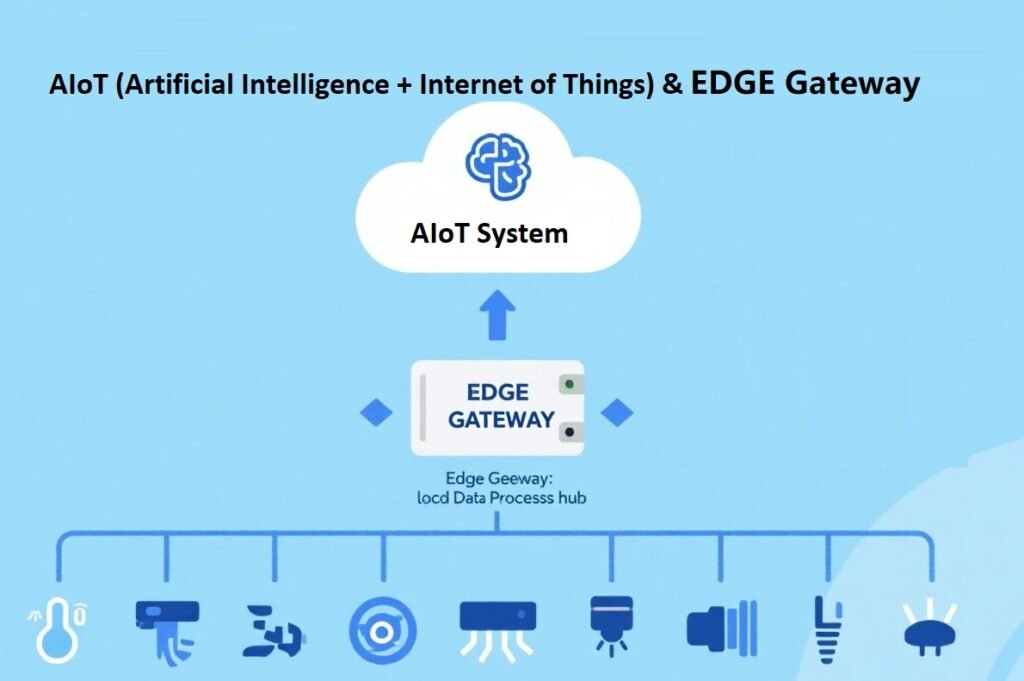
1. What is AIoT?
AIoT (Artificial Intelligence + Internet of Things) refers to a technical system that deeply integrates artificial intelligence (AI) technology with the Internet of Things (IoT).
- Core Logic: The IoT is responsible for “perception” and “connection” (collecting data through sensors and devices and transmitting it), while AI takes charge of “analysis” and “decision-making” (processing data via algorithms to achieve independent judgment, prediction, or control).
- Objective: To upgrade the IoT from “passive data collection” to “active intelligent response”. For instance, smart homes collect environmental data (temperature, humidity, human activity) through sensors, and then AI algorithms automatically adjust air conditioners and lights; industrial equipment realizes fault prediction (instead of post-fault maintenance) via AIoT.
- Technical Scope: It covers sensors, communication networks (5G, WiFi), cloud computing, edge computing, AI algorithms (machine learning, deep learning), etc., and is a comprehensive cross-domain system.
2. What is an Edge Gateway?
An Edge Gateway is a hardware device or functional module located between the “device side” and the “cloud side” in the IoT architecture, and it is a core component of the “edge layer” of the IoT.
- Core Functions:
- Local Data Processing: Filtering, cleaning, and analyzing data near the devices (edge side) to reduce the amount of data uploaded to the cloud (avoiding redundant data occupying bandwidth).
- Protocol Conversion: Being compatible with communication protocols of different devices (such as Bluetooth, ZigBee, Modbus) to realize data intercommunication among heterogeneous devices.
- Edge Computing Support: Running lightweight AI algorithms or logics to achieve rapid local responses (e.g., immediately shutting down equipment when an abnormality occurs without waiting for instructions from the cloud).
- Data Forwarding: Encrypting and transmitting the processed key data to the cloud, and at the same time receiving instructions from the cloud and sending them to the devices.
- Role: It solves problems in the IoT such as “high data transmission latency, heavy cloud load, and unstable networks”. For example, production line equipment in a factory generates massive real-time data, and the edge gateway can locally analyze the data and quickly adjust equipment parameters without relying on the cloud, thereby improving response speed.
3. Core Differences Between AIoT and Edge Gateways
The differences between the two can be compared from the following dimensions:
Comparison Dimension | AIoT | Edge Gateway |
Nature | A macroscopic technical system (integration of AI and IoT) | A specific functional component (device/module in the IoT edge layer) |
Technical Scope | Covers AI algorithms, IoT, cloud computing, edge computing, etc. | Focuses on data forwarding, protocol conversion, and edge computing support |
Role in Architecture | An overall technical framework that guides the intelligent upgrading of the IoT | An “intermediate layer component” in the architecture that supports the operation of the IoT |
Dependency Relationship | May rely on edge gateways (to improve data processing efficiency) | An optional component in the AIoT architecture (but necessary in most scenarios) |
Application Example | Full-process intelligent management and control of smart factories (perception + analysis + decision-making) | A local data processing unit connecting equipment and the cloud in a factory |
4. Cooperative Relationship Between the Two
Edge gateways are important supporting components in the AIoT architecture:
- AIoT needs to process massive amounts of real-time data. If all data is uploaded to the cloud for analysis, it will lead to high latency and high costs. Through “local data processing + edge AI computing”, edge gateways can reduce the response speed of AIoT from the “second level” to the “millisecond level” while reducing the load on the cloud.
- For example, in the AIoT system of self-driving cars, edge gateways are responsible for locally processing data from cameras and radars (such as identifying obstacles) and quickly controlling braking without waiting for instructions from the cloud. This is exactly the key support provided by edge gateways for AIoT.
In summary, AIoT is a comprehensive technical system of “Artificial Intelligence + Internet of Things”, which pursues the intelligent decision-making of devices; edge gateways are functional components in the edge layer of the IoT, which are responsible for local data processing and connection. The two have a relationship of “system” and “component”, and edge gateways provide key support for the efficient operation of AIoT.
