4G connectivity in vending machine
In the era of rapid digital transformation, self-service vending machines have become an integral part of the retail landscape, offering convenient and efficient shopping experiences to consumers. 4G technology, with its reliable connectivity, high-speed data transfer, and wide coverage, plays a crucial role in enhancing the functionality and performance of these machines, while also contributing to the promising market prospects of the self-service vending industry.

4G Application Scenarios in Self-Service Vending Machines
One of the primary applications of 4G in self-service vending machines is real-time data transmission. Vending machines are equipped with sensors that monitor various aspects, such as inventory levels, product temperatures (for machines selling perishable items), and machine operational status. With 4G connectivity, this data can be instantly sent to a central management system. For example, when a product is sold, the inventory sensor detects the change and transmits the information, including the product name, quantity sold, and remaining stock, to the cloud server via 4G. This real-time data allows operators to manage inventory effectively, restock machines promptly, and avoid situations of product shortages or overstocking.
4G also enables seamless user interaction and payment processing. Consumers today expect quick and convenient payment methods. With 4G, self-service vending machines can support various contactless payment options, such as mobile wallets (e.g., Apple Pay, Alipay) and credit/debit card payments. When a user initiates a payment, the transaction data is securely transmitted over the 4G network to the payment gateway for verification and processing. The low latency of 4G ensures that the payment process is fast, reducing waiting times for customers and enhancing their overall shopping experience. Additionally, 4G allows vending machines to display dynamic advertisements and promotional content on their screens. Operators can remotely update these displays based on customer demographics, time of day, or marketing campaigns, thereby increasing sales opportunities.
Remote management and maintenance are another significant benefits brought by 4G. Service providers can monitor the operational status of vending machines from a central control center. 4G enables technicians to access diagnostic information, such as power consumption, machine errors, and component malfunctions. In case of any issues, they can remotely troubleshoot problems, reducing the need for on-site visits. For instance, if a vending machine experiences a dispensing failure, the system can detect the error and send an alert to the maintenance team via 4G. Technicians can then analyze the data, identify the root cause, and even attempt to fix the problem remotely by sending software updates or adjusting settings. This remote management capability significantly improves the efficiency of machine maintenance, minimizes downtime, and ensures continuous service availability.
Network Topology of 4G in Self-Service Vending Machines
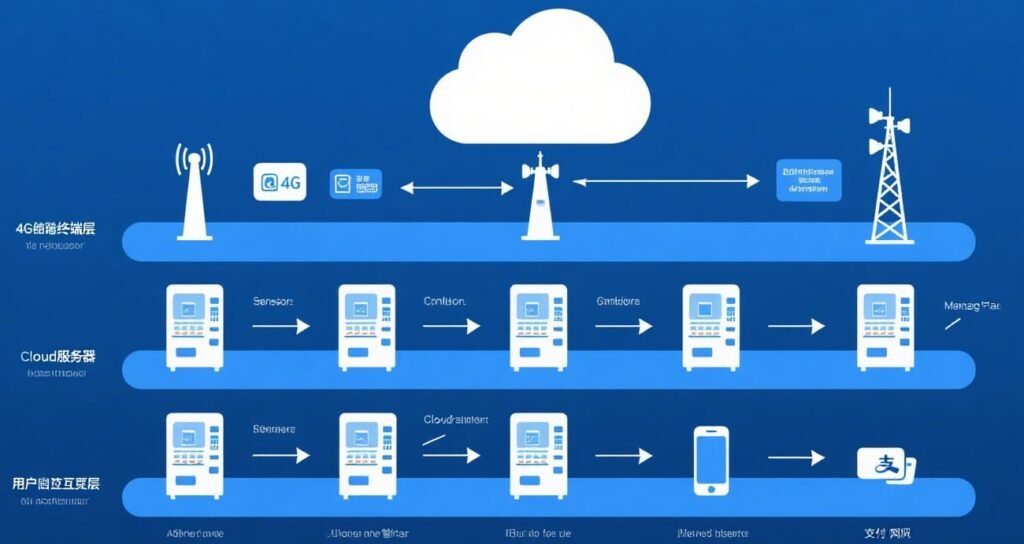
The network topology of 4G in self-service vending machines consists of several interconnected layers:
Terminal Layer
At the base, self-service vending machines serve as the terminal devices. These machines are equipped with sensors (inventory sensors, temperature sensors), control units, display screens, payment terminals, and 4G industrial router. The sensors collect data about the machine’s internal state, the control unit manages operations like product dispensing and payment processing, and the 4G router establishes a connection with the external network.
4G Network Layer
Above the terminal layer is the 4G network infrastructure. Vending machines connect to 4G base stations, which are responsible for receiving data from the machines’ 4G router and forwarding it to the next stage. The 4G network provides the required bandwidth and stable connection to ensure smooth communication.
Cloud Server and Management Layer
Data transmitted from the vending machines via 4G reaches the cloud server. Here, the data related to inventory, sales, user transactions, and machine status is stored and processed. Operators access this data through management platforms, which allow them to monitor all vending machines in the network, analyze sales trends, and manage inventory across different locations.
User Interaction Layer
On the consumer side, mobile applications (if applicable) and payment gateways communicate with the cloud server over the 4G network. Customers can use apps to locate nearby vending machines, check product availability, or receive promotional offers. Payment gateways handle transactions, ensuring secure data transfer between the vending machines and financial institutions.
Market Prospects of Self-Service Vending Machines
The market for self-service vending machines is poised for significant growth. The increasing demand for convenient and contactless shopping experiences, accelerated by factors such as the rise of urbanization and busy lifestyles, provides a strong impetus for the expansion of vending services. Additionally, technological advancements, especially the integration of 4G and future 5G technologies, are enhancing the capabilities of vending machines, making them more intelligent and user-friendly.
The versatility of self-service vending machines also contributes to their promising future. They can be deployed in various locations, including offices, schools, hospitals, transportation hubs, and remote areas, reaching consumers where traditional retail may not be accessible. Moreover, with the ability to offer a wide range of products, from snacks and beverages to daily necessities and even fresh produce, vending machines are becoming more than just a convenience—they are evolving into essential retail outlets.
The integration of data analytics, enabled by 4G connectivity, further boosts the market potential. By analyzing sales data, consumer preferences, and machine performance, operators can optimize product assortments, pricing strategies, and machine placement, thereby increasing profitability. As the vending industry continues to innovate and adapt to changing consumer needs, self-service vending machines are expected to play an even more significant role in the global retail ecosystem in the coming years.
In conclusion, 4G technology is a key enabler for the advanced functionality of self-service vending machines, facilitating seamless data transmission, user interaction, and remote management. Coupled with the industry’s promising market prospects driven by technological advancements and changing consumer demands, self-service vending machines are set to thrive and reshape the retail landscape.
Typical Use Case:
Foxconn Self-service Vending Machine projects, from 2015 to 2017, 13,260 units in total.
R2100 4G Industrial Router

