How can 5G enhance healthcare?
1. Introduction
The convergence of 5G technology and telemedicine is revolutionizing the healthcare industry. 5G, with its ultra – high – speed, low – latency, and massive machine – type communication capabilities, addresses the long – standing challenges in traditional telemedicine, such as network delays and limited data transfer rates. This application plan explores how 5G can be effectively utilized in various telemedicine scenarios.

2. Key 5G – Enabled Telemedicine Applications
2.1 Remote Consultation
- High – Definition Video Conferencing: 5G’s high – speed data transfer enables seamless 4K or even 8K video consultations. For example, in 2025, a patient in a remote Alaskan village was able to connect with a top cardiologist in a large urban hospital in the lower 48 states via 5G – powered video conferencing. The clear video allowed the cardiologist to closely observe the patient’s facial expressions related to chest pain, which was crucial for accurate diagnosis. In another instance, in rural India, Apollo Hospitals, in collaboration with the Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO), used 5G to conduct real – time, high – definition video consultations between doctors and patients in remote areas. This significantly improved the accuracy of diagnoses and reduced the need for patients to travel long distances for consultations.
- Real – Time Data Sharing: Medical images like X – rays, MRIs, and CT scans, which are often large in size (several gigabytes), can be transmitted instantaneously over 5G. In a case in a UK hospital network, a radiologist in London could quickly share a complex MRI image of a brain tumor with a neurosurgeon in Edinburgh for a joint consultation. The high – speed data transfer via 5G ensured that the neurosurgeon could review the detailed image in real – time and discuss the best treatment approach with the radiologist without delay.
2.2 Remote Surgery
- Precise Robot – Assisted Surgery: The ultra – low latency of 5G (as low as 1 millisecond) is a game – changer for remote surgery. In July 2024, a world – first was achieved when a renowned surgeon in Shanghai, China, used 5G to remotely operate a robotic surgical system to perform a lung tumor resection on a patient in Xinjiang, over 5000 kilometers away. The high – speed and reliable 5G connection ensured that the surgeon’s every movement was accurately translated into the actions of the robotic arms, allowing for precise incisions, tissue manipulation, and suturing. In 2025, in the United States, a similar feat was accomplished when a surgeon in California remotely performed a complex orthopedic surgery on a patient in New York using 5G – enabled robotic surgical equipment.
- Enhanced Surgical Guidance: 5G also enables the real – time transmission of high – definition surgical videos and vital patient data to a team of experts who can provide guidance during the surgery. During a complex heart bypass surgery in a large teaching hospital in Europe, the primary surgeon received real – time advice from a cardiologist on the best approach based on the patient’s live heart function data transmitted via 5G. The cardiologist, who was located in a different city, could view the surgical field in high definition and offer immediate suggestions to improve the surgical outcome.
2.3 Remote Patient Monitoring
- Wearable Device Connectivity: 5G – enabled wearable devices, such as smartwatches and health patches, can continuously monitor patients’ vital signs. In a large – scale trial in Singapore, patients with chronic diseases like diabetes and heart disease wore 5G – connected wearable devices at home. The healthcare team could remotely monitor their conditions in real – time. For example, when a diabetic patient’s blood glucose level suddenly dropped to a dangerous level, the healthcare provider received an alert via the 5G – connected system and was able to provide timely advice on treatment, such as taking a glucose – rich drink. In Germany, the 6G Health Institute built a mobile 5G hospital network using 5G slicing, allowing for secure roaming of patients from the ambulance to the emergency room, within the clinic campus, and to the hospital and home while continuously monitoring their vital signs.
- Expanded Monitoring Range: With 5G’s massive machine – type communication, a large number of patients can be monitored simultaneously. In a post – disaster medical relief effort in a flood – affected area in Bangladesh, many injured people were equipped with 5G – connected monitoring devices. The data from these devices was aggregated and analyzed in real – time to identify trends and make informed decisions about resource allocation. This helped medical teams prioritize treatment and ensure that patients received the necessary care promptly.
3. Technical Requirements and Deployment Considerations
3.1 Network Infrastructure
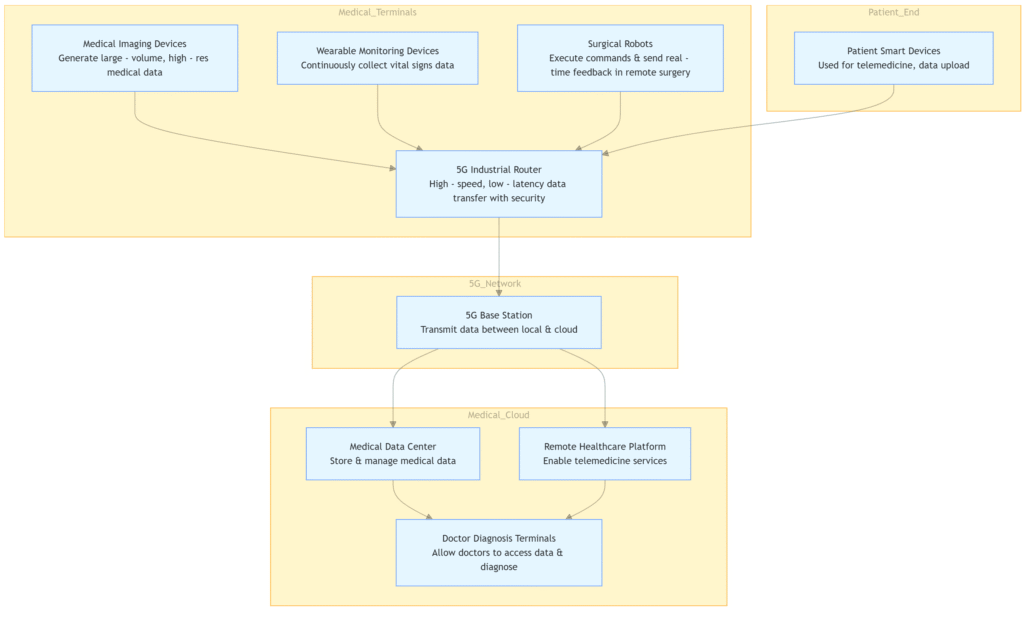
- 5G Base Station Deployment: Healthcare institutions need to ensure sufficient 5G base station coverage. In urban areas, this may involve working with telecommunications companies to optimize existing 5G networks. In rural or remote areas, additional base stations may need to be installed to provide reliable connectivity for telemedicine applications. For example, in some remote villages in Africa, mobile network operators, in partnership with international aid organizations, have installed 5G base stations to enable telemedicine services. These base stations have allowed local healthcare workers to connect with specialists in larger cities for consultations and remote patient monitoring.
- Network Slicing: To guarantee the quality of service for critical telemedicine applications, network slicing can be implemented. This technology divides the 5G network into multiple virtual networks, each with its own dedicated resources. For remote surgery, a high – priority network slice can be allocated to ensure low latency and high – bandwidth connectivity, separate from other less critical data traffic in the hospital. In a large hospital in South Korea, network slicing has been successfully implemented, allowing for seamless remote surgeries and high – definition video consultations without interference from other network activities within the hospital.
3.2 Data Security and Privacy
- Encryption Technologies: Given the sensitive nature of medical data, strong encryption algorithms must be used to protect data during transmission over 5G networks. For example, end – to – end encryption can be applied to ensure that patient medical records, images, and video consultations are secure. This prevents unauthorized access and data breaches. In the European Union, strict data protection regulations under GDPR require healthcare providers to implement such encryption measures. Many healthcare institutions across Europe have adopted advanced encryption technologies to comply with these regulations and safeguard patient data.
- Compliance with Regulations: Healthcare providers must comply with relevant data protection regulations, such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the United States. This includes implementing proper access controls, data storage, and security audit mechanisms to safeguard patient privacy. In the US, hospitals and healthcare providers are constantly audited to ensure compliance with HIPAA, and failure to do so can result in significant fines. To meet these requirements, many institutions have implemented comprehensive data security policies and procedures, including regular staff training on data privacy and security.

4. Challenges and Solutions
4.1 Cost
- Initial Investment: The deployment of 5G infrastructure and the acquisition of 5G – compatible medical devices can be costly. To address this, healthcare institutions can seek partnerships with telecommunications companies, government subsidies, or explore leasing options for medical devices. For example, in some developing countries, the government has provided subsidies to healthcare facilities to help them upgrade to 5G – enabled telemedicine systems. In addition, some medical device manufacturers offer leasing programs for 5G – enabled remote monitoring devices, reducing the upfront financial burden on hospitals.
- Ongoing Operational Costs: The cost of maintaining 5G networks and software updates also needs to be considered. Institutions can optimize costs by negotiating favorable service contracts with network providers and implementing energy – efficient 5G equipment. In some large hospital networks, they have negotiated long – term service contracts with network providers, which include provisions for regular software updates and maintenance at a fixed cost. Additionally, they have started using energy – efficient 5G base stations and equipment to reduce power consumption and operational costs.
4.2 Technical Expertise
- Staff Training: Healthcare professionals may lack the technical knowledge to operate and troubleshoot 5G – enabled telemedicine systems. Training programs should be developed to educate medical staff on using new devices and software. For example, many hospitals in Australia have organized workshops and online training courses to teach doctors and nurses how to use 5G – powered remote consultation platforms and interpret data from 5G – connected wearable devices. These training programs have been well – received by the staff, and they have reported increased confidence in using the new technology.
- Technical Support Teams: Establishing in – house or external technical support teams is essential. These teams can quickly respond to network issues, software glitches, and device malfunctions, ensuring the smooth operation of telemedicine services. In a large healthcare system in Canada, they have an in – house technical support team that is on call 24/7. The team is trained to handle a wide range of technical issues related to 5G – enabled telemedicine systems, from network connectivity problems to software bugs, and they can provide immediate solutions to keep the services running smoothly.
5. Conclusion
The integration of 5G in telemedicine has the potential to transform healthcare delivery, making it more accessible, efficient, and patient – centered. By leveraging 5G’s capabilities in remote consultation, surgery, and patient monitoring, healthcare providers can overcome geographical barriers and provide high – quality care to patients everywhere. However, addressing challenges related to cost, technical expertise, and infrastructure is crucial to fully realize the benefits of this revolutionary technology in the healthcare industry.
